The CFO Scenario That Should Keep You Up at Night
Picture this: It is Thursday afternoon. Your CFO has a board meeting at 9 AM Friday. She has 47 pages of quarterly financials — revenue by division, margin by product line, pending acquisition targets, pre-announcement earnings figures — and she needs a crisp executive summary by end of day.
So she does what millions of knowledge workers do every single day in 2026: she opens ChatGPT, pastes the entire financial document into the chat box, and types "summarize this for the board."
She gets a brilliant two-page summary in 45 seconds. The meeting goes flawlessly. Nobody in the room knows that your company's pre-announcement earnings, unreleased acquisition strategy, and internal margin data just traveled through OpenAI's servers — and depending on your account type and their current data retention policies, may have been used to train future models.
This Is Not Hypothetical
Your CFO is not malicious. She is not even negligent by her own estimation. She is doing what every human being does when handed an incredibly powerful tool with no guardrails: she uses it. The problem is not your employees. The problem is your security architecture.
This is the shadow AI crisis, and in 2026, it is the single largest unaddressed data liability for small and mid-sized businesses. Learn how we address it with our Secure AI Gateway — or read on to understand the full scope of the threat.
Shadow AI by the Numbers
The research on shadow AI usage is consistent across every major survey: your employees are using unauthorized AI tools. The only question is how much of your sensitive data has already walked out the door.
Let that sink in: 77% of employees who use AI tools paste sensitive business data into them. They are not browsing — they are submitting your most valuable information to third-party systems with no visibility, no controls, and no audit trail on your end.
Gartner's 2030 Prediction
The math is brutal. If 78% of your employees are using shadow AI, and 77% of those are pasting sensitive data, and your average breach cost is $4.44M with a $670K premium for AI-involved incidents — you are carrying a seven-figure liability you probably cannot see in any security dashboard you own right now.
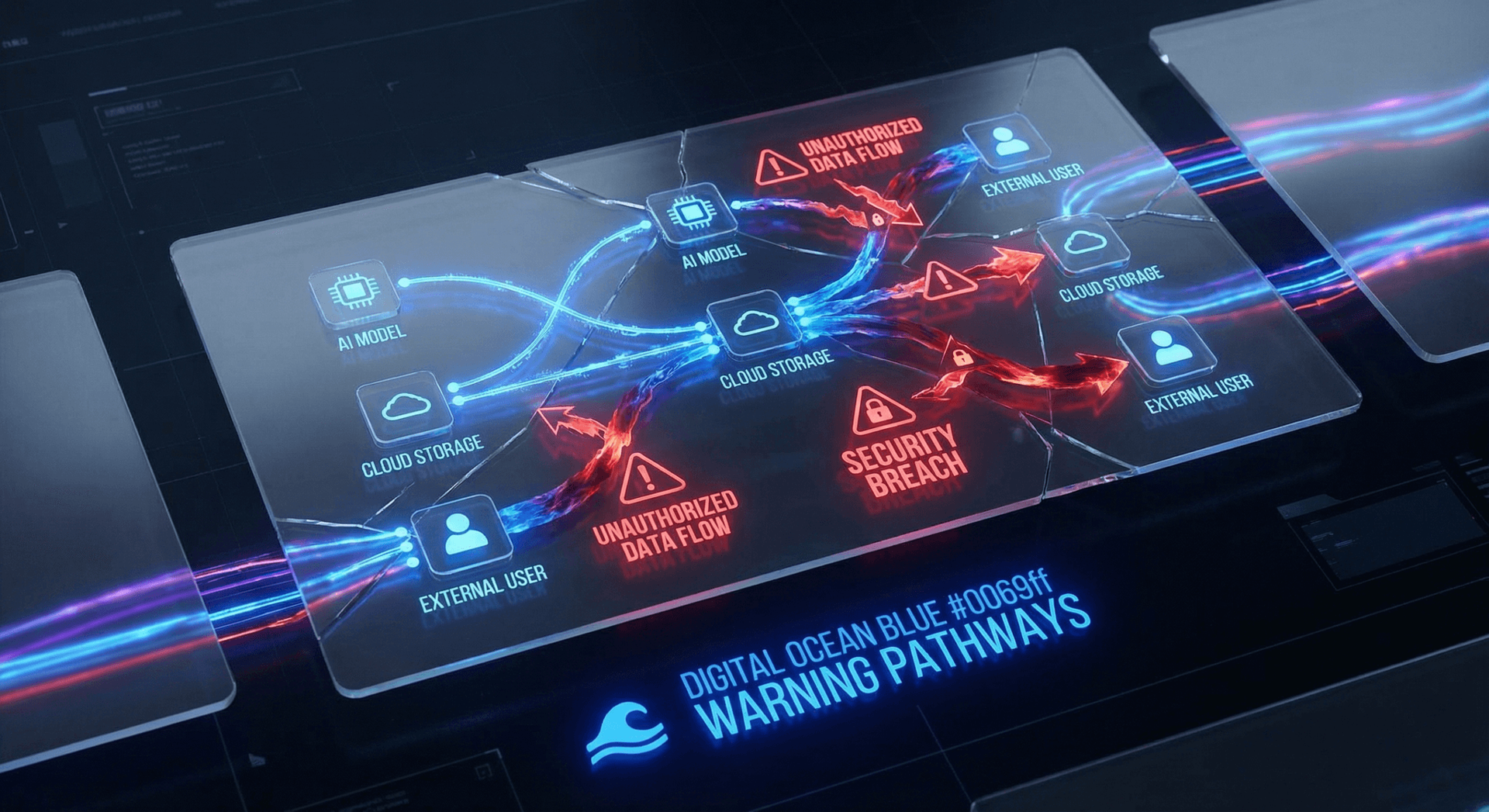
What Actually Leaves the Building
When employees use consumer AI tools without authorization, the data that flows through those systems spans virtually every sensitive category your business handles. Here is what the LayerX research found employees actually submit:
Financial Data
Revenue figures, margin analysis, budget spreadsheets, earnings projections, acquisition targets, compensation data, and investor materials. This is the CFO scenario — and it happens daily in businesses of every size. For publicly traded companies, this can constitute material non-public information (MNPI), triggering SEC liability.
Customer and Patient Data
Names, email addresses, purchase histories, medical records, insurance information, and support tickets. Your customer service team uses AI to draft responses — and they paste the customer's full profile to get context. Every paste is a potential HIPAA violation, a PCI-DSS incident, or a state privacy breach.
Intellectual Property
Source code, product roadmaps, trade secrets, manufacturing processes, proprietary formulas, and competitive strategy documents. Your developers use AI for code review. Your product team uses it for roadmap analysis. Every session potentially exposes what makes your business unique.
Legal and HR Materials
Employment contracts, pending litigation details, settlement terms, performance reviews, disciplinary records, and confidential communications. HR uses AI to draft sensitive employee communications. Legal uses it to summarize case materials. Attorney-client privilege does not survive submission to a third-party AI platform.
The common thread is intent: none of these employees mean to cause a breach. They are trying to do their jobs faster and better. The problem is the architecture — consumer AI tools are not designed for enterprise data governance, and using them for business data is like running payroll through your personal Gmail account.
Compliance Exposure: HIPAA, SOX, PCI-DSS, Indiana
Shadow AI does not just create abstract security risk — it creates concrete, documentable, regulatorily-actionable violations. Here is what each major framework requires and how shadow AI breaks it:
HIPAA — Healthcare Data
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act requires covered entities to maintain Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with any third party that handles Protected Health Information (PHI). ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and virtually every consumer AI tool will not sign a BAA.
The violation: When a medical practice's billing coordinator pastes a patient's insurance claim into ChatGPT to help draft an appeal letter, that is an unauthorized PHI disclosure. Penalties range from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with annual caps of $1.9 million per violation category. See our guide on HIPAA-compliant AI deployment.
SOX — Financial Controls
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires public companies to maintain documented controls over financial data and reporting. Submitting pre-announcement financial data to an AI tool that has no audit trail, no access controls, and potentially uses that data for model training is a textbook SOX control failure.
The violation: Material non-public financial information submitted to unauthorized systems. Beyond regulatory penalties, this creates securities liability if the information influences market activity before announcement.
PCI-DSS — Payment Card Data
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard prohibits transmitting cardholder data to any system that is not explicitly within your defined cardholder data environment (CDE). Consumer AI tools are categorically not within any business's CDE.
The violation: A customer service rep pastes a transaction dispute record containing card numbers into an AI tool. Instant PCI-DSS breach. Card brand fines run $5,000 to $100,000 per month until remediation, plus potential loss of the ability to process card payments.
Indiana IC 24-4.9 — State Data Breach Law
Indiana's data breach notification statute (IC 24-4.9) requires businesses to notify affected Indiana residents when their personal information is compromised. A shadow AI incident involving customer data may trigger notification obligations even if the breach was inadvertent.
The violation: Failure to notify can result in civil penalties. More importantly, the reputational damage of notifying thousands of Fort Wayne customers that their data was exposed through an employee's unsanctioned AI session is significant and lasting.

The Training Data Trap
Beyond compliance, there is a subtler threat that most businesses have not fully reckoned with: the training data question. When your employees submit data to consumer AI tools, what happens to that data?
The answer varies by tool, account type, and current policy — and it changes. OpenAI, for example, has had multiple policy changes regarding whether free vs. paid API vs. paid consumer accounts use conversation data for training. The policies are complex, frequently updated, and often not read by the employees clicking through them.
The Uncertainty Is the Problem
The training data concern is most acute for intellectual property. If a competitor's engineer later uses the same AI tool and receives a response that incorporates patterns from your proprietary code, your trade secret protection may be permanently compromised. You cannot un-train a model.
The only way to eliminate training data risk is to use AI tools that explicitly guarantee no training on your data — typically through enterprise agreements with zero-retention provisions, or through on-premise deployment where your data never leaves your infrastructure.
Why Banning AI Does Not Work
The natural response to shadow AI is the policy response: issue a company-wide ban, add it to the acceptable use policy, and call it done. Samsung tried this. JPMorgan tried this. Citigroup tried this. And in every case, employees found workarounds within days.
Here is why bans fail structurally:
- Personal devices bypass corporate controls: Your IT department can block ChatGPT on corporate networks and devices. They cannot block an employee's personal phone on their personal cellular connection during a work task.
- Productivity pressure overrides policy: When an employee has a deadline and AI would save them two hours, the abstract threat of a policy violation loses to the concrete pressure of the deadline every time. You are fighting human nature.
- The tools are invisible: 86% of IT leaders say they cannot see shadow AI usage in their current monitoring. If you cannot detect it, you cannot enforce the ban.
- Bans eliminate the productivity benefit too: The employees who most creatively use AI are often your highest performers. Banning AI does not reduce their AI use — it drives it underground while signaling that you are behind the curve.
- The genie is out of the bottle: In 2026, AI is not a novelty. It is a productivity tool as embedded in workflows as search engines and email. You cannot meaningfully separate knowledge workers from AI any more than you could separate them from Google.
The Delinea Finding

The "Embrace, Don't Ban" Framework
The solution to shadow AI is not fewer AI tools — it is better AI tools, deployed with proper governance. A strategic AI consulting engagement can help you identify the right approach. When your employees have access to a sanctioned, monitored, controlled AI platform that does everything ChatGPT does (and more), the incentive to use unauthorized tools evaporates.
The "Embrace, Don't Ban" framework has three pillars:
Pillar 1: Same Models, Controlled Gateway
Your employees use ChatGPT because it works. GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini are genuinely excellent tools. The problem is not the model — it is the uncontrolled access point. A secure AI gateway routes employee requests through the same underlying models (via API) while applying data loss prevention filters, removing sensitive content before it reaches the model, logging all interactions, and enforcing role-based access policies.
The employee experience is nearly identical. The security posture is entirely different.
Pillar 2: Visibility and Monitoring
You cannot manage what you cannot see. A proper enterprise AI deployment gives you complete visibility: which employees are using AI, what types of requests they are making, what categories of data are being submitted, and where policy violations are occurring. This visibility alone is transformative — most businesses are currently flying blind.
Monitoring also creates a feedback loop: as you see what employees actually need AI for, you can proactively build better workflows and reduce the temptation to go rogue.
Pillar 3: Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Integration
DLP policies automatically detect and redact sensitive content before it leaves your environment. If an employee tries to paste customer records into an AI query, DLP strips the personally identifiable information, substitutes anonymized placeholders, and forwards the sanitized version. The employee gets a useful response. The sensitive data never leaves your perimeter.
For regulated industries, DLP can be configured to enforce HIPAA de-identification standards, PCI-DSS cardholder data rules, and SOX material information controls automatically — without requiring employees to memorize compliance requirements.
The result is a win-win: employees get the AI productivity they need, and you get the security and audit trails that compliance requires. Shadow AI disappears not because you banned it, but because you gave employees something better through a controlled channel. For a detailed technical look at how this works, see our AI Employee security checklist.
The Secure Gateway Solution
Cloud Radix's Secure AI Gateway is built specifically to eliminate shadow AI risk while preserving the productivity benefits your employees have come to depend on. Here is how it works in practice:
- API-level access to enterprise models: Your employees get GPT-4, Claude 3.5, and Gemini Pro — the exact models they are currently using through consumer interfaces — accessed through a controlled API gateway that never touches consumer training pipelines.
- Zero data retention: All queries processed with zero-retention agreements. Your business data is not stored, not logged by the AI provider, and not used for model training. Full stop.
- Real-time DLP scanning: Every submission scanned for PII, PHI, financial data, credit card numbers, and custom-defined sensitive patterns before it reaches the model. Violations are blocked and flagged, not just logged after the fact.
- Complete audit trail: Every AI interaction logged with timestamp, user identity, request category, and DLP policy results. Your compliance team can answer any regulator's question about who submitted what and when.
- Role-based access: Finance team gets financial analysis tools. Medical staff gets HIPAA-compliant health AI. Customer service gets customer interaction tools. Each role's AI capabilities are scoped to their legitimate business need.
- On-premise option: For organizations with the highest data sensitivity requirements, we offer fully on-premise deployment. Your data never leaves your infrastructure. Period.
The Business Case

Shadow AI Risk Assessment Checklist
Use this checklist to assess your current exposure. A "no" to any item indicates active risk that needs to be addressed.
Do you have visibility into which AI tools your employees use?
If you cannot answer which tools and how frequently, you are blind to your exposure.
Do you have technical controls (not just policy) blocking unauthorized AI tools?
Policy alone does not work. You need network-level and endpoint-level controls.
Do you have DLP rules that cover AI tool submissions?
Traditional DLP rules often do not cover web-based AI tools. Verify yours do.
Are all AI vendor relationships documented with appropriate data processing agreements?
BAAs for HIPAA, DPAs for GDPR-adjacent requirements, contractual zero-retention provisions.
Do you have an audit trail of AI interactions for compliance purposes?
Regulators increasingly expect to see logs of AI activity, not just human actions.
Have you trained employees on shadow AI risk and provided a sanctioned alternative?
Training without alternatives creates resentment and drives shadow AI underground.
Are your cyber insurance policies current and do they cover AI-related incidents?
Many legacy policies have AI exclusions. Review yours explicitly.
If you answered "no" or "I don't know" to three or more items, you have a significant shadow AI risk that warrants immediate attention. Start with our AI Employee security checklist for a self-service audit, or our free Shadow AI Risk Assessment walks through your specific environment and identifies the highest-priority gaps. Schedule yours today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1.Is it illegal for employees to use ChatGPT for work?
Not inherently illegal, but it can create legal liability. If an employee submits data that is subject to HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or other regulations through an unauthorized tool, the resulting violation falls on the company — not the employee's individual action.
Q2.Does OpenAI use business data submitted through ChatGPT for training?
It depends on the account type and current policy. ChatGPT Plus (consumer) has had varying policies. ChatGPT Team and Enterprise claim not to use data for training, but these require paid accounts with specific settings. API access with zero-retention options is the only way to get contractual guarantees.
Q3.We're a small business. Is shadow AI really a risk for us?
Yes — potentially more so. Large enterprises have dedicated security teams and compliance infrastructure. Small businesses are less likely to have DLP controls, vendor agreements, or monitoring in place. And regulators do not size penalties to company size for HIPAA violations.
Q4.How do we know which AI tools our employees are using?
Without technical controls, you likely do not. Network traffic analysis, endpoint monitoring, and browser extension audits can reveal AI tool usage. A Shadow AI Risk Assessment typically starts with this discovery phase.
Q5.Can we just block ChatGPT on our corporate network?
You can block it on your corporate network and managed devices. But employees can access it via personal devices, cellular connections, or VPNs. Technical blocking addresses the most casual usage but does not eliminate the risk — and it does not provide a sanctioned alternative.
Q6.What is the difference between a secure AI gateway and just using ChatGPT Enterprise?
ChatGPT Enterprise addresses OpenAI's data retention for OpenAI's tools. A secure gateway gives you visibility and control across all AI tools, applies your DLP policies consistently, integrates with your existing security stack, and provides a unified audit trail — regardless of which underlying models are used.
Sources
- WalkMe — 2025 Shadow AI & Digital Adoption Report
- IBM Security — Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025
- LayerX — 2025 Enterprise GenAI Security Report
- Delinea — State of Privileged Access & AI Security 2025
- ISACA — State of Cybersecurity 2025: AI & Shadow IT
- Gartner — Predicts 2026: AI Data Security and Shadow AI
- HHS — HIPAA Penalty Structure and Enforcement
- Indiana Code — IC 24-4.9 Data Breach Notification Law
Get Your Free Shadow AI Risk Assessment
Find out exactly which AI tools your employees are using, what data has been exposed, and how to close the gaps — before a regulator or breach does it for you.


